Diabetic Retinopathy Prevention and Management: What Patients Should Know
With an estimated 15.9 million Americans age 65 or older now living with diabetes, it remains a major health threat, especially for eye and vision health. That’s because you may be at risk for diabetic retinopathy if you have type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes (during pregnancy).
The longer you’ve had diabetes, the greater your chances of diabetic retinopathy development. And while there is no cure, there are ways to reduce your risk, including managing your diabetes and blood sugar levels.
Delving Into Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes causes your blood sugar (glucose) to increase, and over time, it can damage the retina’s blood vessels. This is serious, as the retina converts light and images into nerve signals that are sent to the brain, enabling us to see. Diabetic retinopathy can also result in fluid and blood leaking into the retina, as well as retinal hemorrhages, or excessive bleeding.
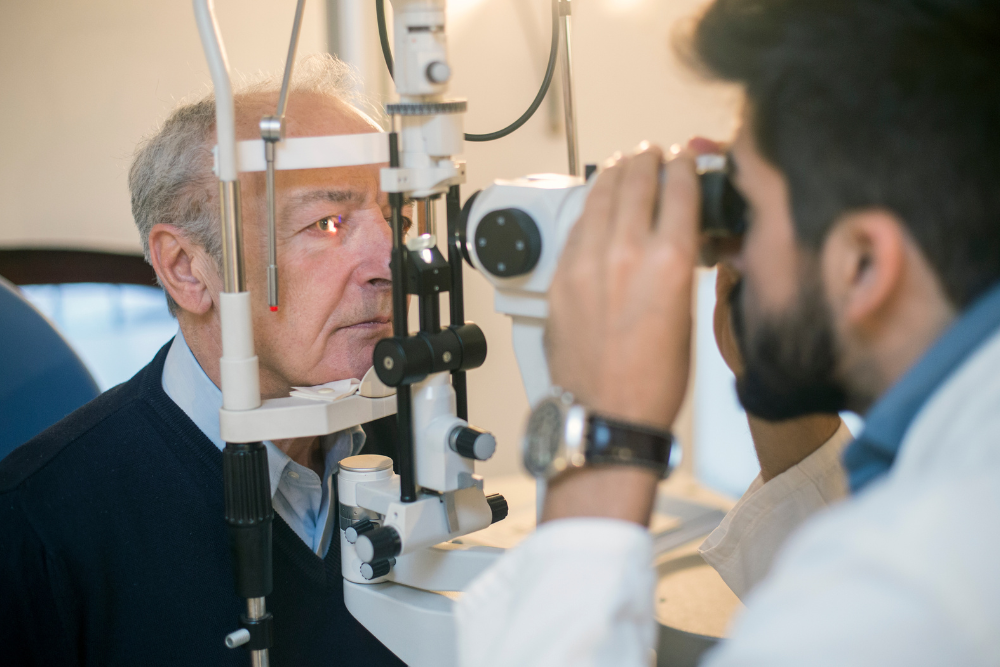
Schedule Diabetic Retinopathy Eye Exams
As diabetic retinopathy can progress to a more serious form, regular screening eye examinations become even more important with age. We recommend that older adults with diabetes have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year. This schedule allows your ophthalmologist to detect and diagnose you earlier.
You also need to monitor your vision and tell your doctor about sudden changes, such as blurry, spotty, or hazy vision. If you see dark, floating spots or cobweb-like streaks, get immediate medical treatment. Known as floaters, these symptoms can be a sign of a retinal tear or impending retinal detachment, which is a medical emergency that can cause permanent vision loss if not addressed immediately.
Healthy Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure Benefits Diabetic Retinopathy
Proper diabetes management may reduce your risk of diabetic retinopathy and related vision loss. You need to take your insulin and any other medications regularly. You’ll also have to maintain healthy glucose levels and test your glucose levels several times each day.
Your doctor can provide a glycosylated hemoglobin test (hemoglobin A1C), which details your average blood sugar levels for the previous two to three months. Your goal should be an A1C below 7 percent. You must also ensure healthy blood pressure, with a level of less than 130/80 mm Hg advised for adults with diabetes.
Plan Your Diet With Diabetic Retinopathy In Mind
Research suggests that proper diabetes management is associated with a diet rich in nutrients and low in fat and calories. This may promote weight loss, which improves blood glucose control. You should also consume three meals a day, at regular times, as this helps your body better use insulin. Here are additional dietary guidelines:
- Healthy carbohydrates, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes (beans, peas), and low-fat dairy products. Avoid foods or drinks with added fats, sugars, and sodium.
- Dietary fiber, like fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, and whole grains, regulate your body’s digestion and help control blood glucose levels.
- Heart-healthy fish should be eaten at least twice a week. Such fish as salmon, tuna, and sardines are rich in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Fats with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats help reduce cholesterol levels, and examples include avocados, nuts, canola, and olive oils.
Diabetic patients should also reduce their salt, caffeine, and alcohol intake. You should also consume no more than 200 milligrams (mg) of cholesterol a day, and no more than 2,300 mg of sodium a day.
When it comes to diabetic retinopathy, proper diabetes management is crucial. If you are in South Carolina and would like to schedule an appointment with a diabetic eye specialist, we encourage you to contact Palmetto Retina Center with any questions or concerns.
